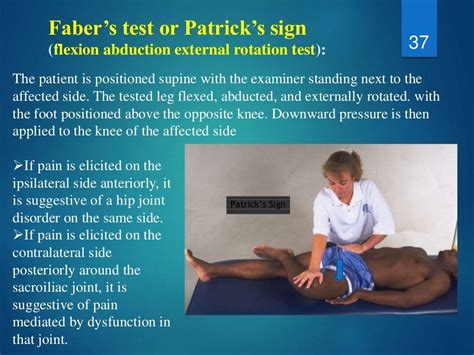
lateral pelvic compression test|gaenslen's test positive : distribute Evaluate the Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve (LFCN) as a cause of thigh pain. Concept of test. LFCN is compressed by the inguinal ligament. A downward force to the hip will relax the ligament and temporarily alleviate the patient’s symptoms. Resultado da Explore. shadman. Create with DreamUp. This century. Treat yourself! Core Membership is 50% off through February 29. Upgrade Now. Want to .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web741 avaliaç ões. R$ 419,90. 4%. R$ 399,99 8x de R$ 49,99 sem juros no cartão de crédito. Formas de pagamento: cartões de crédito Ame, Mastercard, Visa, Elo, American Express, Aura, Diners Club, Hipercard; boleto bancário; Ame Digital; Pix. Todas as regras e promoções são válidas apenas para produtos vendidos e entregues pelo Shoptime.
positive thigh thrust test
Evaluate the Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve (LFCN) as a cause of thigh pain. Concept of test. LFCN is compressed by the inguinal ligament. A downward force to the hip will relax the ligament and temporarily alleviate the patient’s symptoms. Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT .
Pelvic ring fractures are high energy fractures of the pelvic ring which typically occur due to blunt trauma. Diagnosis is made radiographically with pelvic radiographs and further characterized with CT scan.
custom moisture meter testing
Pelvic Instability on Compression. Suggests unstable Pelvic Fracture in the setting of significant Trauma; Apply Pelvic Binder if Unstable Pelvic Fracture is suspectedWith the patient lying on his side, examiner should stand beside the patient with both hands on the patient’s lateral trunk (side of the rib cage) that is up. With patient standing, sitting, or lying .Lateral compression type-1 pelvic fractures are a common fragility fracture in older adults. Patients who do not mobilise due to ongoing pain are at greater risk of immobility-related . summary. Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction is a degenerative condition of the sacroiliac joint resulting in lower back pain. Diagnosis is made clinically with pain just inferior to the posterior superior iliac spine that is made worse with .
A positive pelvic compression test and Tinel's sign can be used to identify those with lateral femoral cutaneous nerve entrapment. 30 The pelvic compression test involves applying a .Physical exam findings are based on provocative maneuvers in which criteria usually calls for three or more being positive. These include distraction test, compression test, Gaenslen .
Results. Over an 11-year period (2004–14), 134 patients suffered from lateral compression fractures out of 567 pelvic fractures (33%). After excluding patients with clear indications for operation (complex pelvic fractures and pubic symphysis ruptures) and pediatric fractures, 114 patients could be included in the analysis.Meralgia paraesthetica is due to compression or traction of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve in its pathway from the lumbar plexus, L2-3. . The pelvic compression test is usually positive (this involves deep palpation in the .
Description and Purpose [edit | edit source]. The SIJ (Sacroiliac Joint) Distraction (Colloquially know as Gapping) test is used to add evidence, positive or negative, to the hypotheses of an SIJ sprain or dysfunction when used in the Laslett SIJ Cluster testing.This test stresses the anterior sacroiliac ligaments. This test has also been described as the Transverse Anterior Stress Test .Performing the Test: With patient standing, sitting, or lying supine, use both hands to compress the lateral sides of the rib cage inward towards the sternum. With the patient lying on their side, use both hands on the lateral side of the rib cage that is facing upward to compress the ribcage towards the table. Positive Test Fragility fractures of the pelvis affect approximately 600,000 adults each year [1,2,3].The incidence and costs of fragility fractures of the pelvis are rising faster than other fragility fractures of the hip, spine, and wrist [2,3,4].Lateral compression (LC) type pelvic ring injuries are the most common type of fragility fracture of the pelvis, making up 80% of pelvic . Rarely, pressure on the lateral cutaneous femoral nerve can arise from a mass in the retroperitoneal space - eg, tumours, iliacus haematoma. 9. Investigations. The pelvic compression test is highly sensitive and the diagnosis can often be made with this test alone. 7. Injection of the nerve with local anaesthetic will abolish the pain.
Diagnosing pelvis somatic dysfunction: Symptoms, Causes, Videos & Quizzes | Learn Fast for Better Retention! . The side of the dysfunction is determined by the superior PSIS. Alternatively, perform the ASIS compression test, with the patient supine, by compressing bilaterally anterior to posterior at the ASIS. . Lateral on L: Level: Pubic .Significant deformity of lateral compression injuries may require reduction and fixation, even if little instability is evident. Internal rotation of the hemipelvis can produce deformity which may obstruct the pelvic outlet, limit external rotation of the hip joint, or be unsightly.
The lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (LFCN) of the thigh is normally a branch of the posterior disunity of the L2 and L3 spinal nerves. It travels through the pelvis heading towards the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) and exits the lesser pelvis .
A painful mononeuropathy of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (LFCN), meralgia paresthetica is commonly due to focal entrapment of this nerve as it passes through the inguinal ligament. . (pelvic compression testing) reproduces the symptoms. A study in 45 patients found that the pelvic compression test had a sensitivity of 95% and a .
Home Meralgia Paresthetica – Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Neuropathy pelvic compression test. pelvic compression test. Download article as PDF. Photo is courtesy www.sportinjuriesandwellnessottawa.blogspot.com. Search This Site. Social Counter. 47 Followers Follow. 12,200 Subscribers Subscribe. Lateral compression injuries often occur when the pelvis is impacted by a vehicle. Vertical pelvis injuries usually result from falls or injuries involving an axial load. While mortality rates range from 1% to 15% in closed fractures, they can escalate to 50% in open fractures, with hemorrhage being the primary cause of death. more common after lateral compression pelvic ring injuries. Genetics. HLA-B27. associated with ankylosing spondylitis. Associated conditions. orthopaedic conditions. lumbar spinal fusion. post-traumatic arthritis. . SI compression test. performed with patient laying lateral on exam table. Introduction. Lateral compression type I (LC-1) injuries of the pelvic ring represent the most common type of pelvic ring disruptions. The mortality rate associated with LC-1 injuries has been reported to range from 5.1 % [] to 8.6 % [].Their relationship to injury of intra-pelvic structures is also well known [].The prevalence of LC-1 pelvic fractures has been .

Background: Occult instability of lateral compression type-1 (LC1) pelvic ring injuries may be determined with a fluoroscopic stress examination under anesthesia (EUA) performed in the operating room. We hypothesized that LC1 injuries, similar to some fractures of the extremities, could be radiographically stressed for stability in the emergency department (ED).Entrapment of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve usually in the inguinal canal; Etiology. Intrapelvic (pregnancy, enlarging mass, aneurysm) Extrapelvic (trauma, tight garment or belt, obesity) Systemic ; Clinical Features. Numbness and pain of anterolateral thigh Usually unilateral with subacute onset; Pelvic compression test Turn patient on sideTake the quiz to test your expertise! > Lateral Compression Type 1 Pelvic Fractures in Elderly Anticoagulated Patients resource center. Menu. . and daily 325-mg aspirin therapy. On physical examination, he was in pain, and .
Pelvic Compression Testing. The pelvic compression test is a diagnostic tool that involves placing the patient in the lateral recumbent position while an external downward force is applied with the examiner’s hands over the lateral aspect of the ASIS. The pressure is held for 45 seconds to determine if the patient’s symptoms improved.Lateral compression type 1 (LC1) fractures are the commonest pelvic ring injury. However, they represent a heterogenous spectrum of injury mechanisms and fracture patterns, resulting in a lack of strong evidence for a universally agreed treatment algorithm. Although consensus exists that .
This article focuses on pelvic fractures that are caused by a high-energy event, such as a car collision. Because the pelvis is in proximity to major blood vessels and organs, this type of fracture may cause extensive bleeding and other injuries that require urgent treatment. . Lateral compression fracture; Vertical shear fracture; Types of .If the test is positive for pain, it could be effective re-assess the aSLR offering a manual compression through the iliac bones or use a belt to stabilize the pelvis. If the pain is reduced with compression, this can guide the physical examination to the hypothesis of MC deficit instead of a sacroiliac joint assessment.
The lateral femoral cutaneous nerve is a pure sensory nerve vulnerable to compression as it passes from the lumbosacral plexus towards the inguinal ligament and into the subcutaneous tissue of the anterior thigh. Meralgia paresthetica is a clinical condition that involves pain and dysesthesia in the anterolateral thigh associated with compression of the lateral . Lateral compression type 1 (LC1) fractures are the commonest pelvic ring injury. However, they represent a heterogenous spectrum of injury mechanisms and fracture patterns, resulting in a lack of strong evidence for a universally agreed treatment algorithm. Although consensus exists that LC1 fractures have a preserved posterior ligamentous complex and are .
Diagnostic maneuvers include the pelvic compression test in which the patient lies on their unaffected side, and the examiner applies downward pressure on the patient’s ilium/pelvis for approximately 45 seconds. A test is positive if symptoms are reduced and has a reported sensitivity and specificity of 95% and 93%, respectively.
Meralgia paresthetica (MP), a neuropathy of the Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve (LFCN), is an uncommon cause of neuropathic thigh pain. Meralgia paresthetica (MP), a neuropathy of the Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve (LFCN), is an uncommon cause of neuropathic thigh pain. . The Pelvic Compression test and Neurodynamic Testing can also be used . Lateral pelvic compression test . Nouraei (2007) Meralgia parasthetica. 95/93.3. a SN sensitivity, SP specificity. Table 2.8. Physical exam tests for pelvic disorders . Test/lead author. Pathology. SN/SP a. 1. Suppine to sit (long sitting test) Bemis (1987) Pelvic dysfunction, pelvic malrotation. Compression has been well accepted as an important . test result is described as pelvic tilt occurring towards the non-weightbearing side and a ‘compensated’ positive test as trunk lateral flexion towards the weightbearing side during single leg stance. . consideration of lateral pelvic tilt alone in the Trendelenburg test, may result .
custom moisture meter testing program
webBanana randomly pairs you with other gay men to chat one on one. Connect, video, and text with other interesting men with similar interests.
lateral pelvic compression test|gaenslen's test positive